
Another method used a trompe to produce compressed air from falling water, which could then be used to power other machinery at a distance from the water.

In hydrology, hydropower is manifested in the force of the water on the riverbed and banks of a river. It is particularly powerful when the river is in flood. The force of the water results in the removal of sediment and other materials from the riverbed and banks of the river, causing erosion and other alterations.
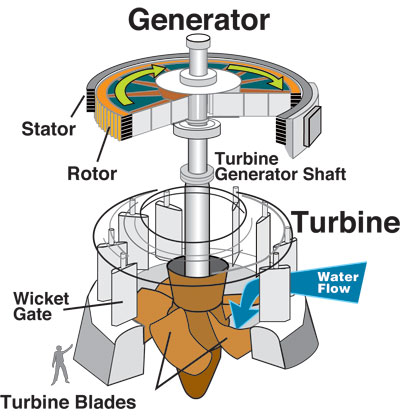
Hydroelectricity is the term referring to electricity generated by hydropower; the production of electrical power through the use of the gravitational force of falling or flowing water. It is the most widely used form of renewable energy. Once a hydroelectric complex is constructed, the project produces no direct waste, and has a considerably lower output level of the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide (CO2) than fossil fuel powered energy plants. Worldwide, an installed capacity of 777 GWe supplied 2998 TWh of hydroelectricity in 2006. This was approximately 20% of the world's electricity, and accounted for about 88% of electricity from renewable sources.








0 comments:
Post a Comment